
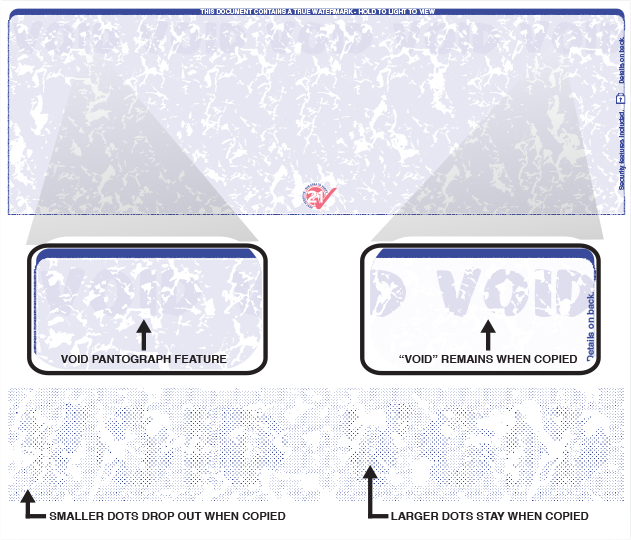
The set of minimum security features would not only ensure uniformity across all cheque forms issued by banks in the country but also help presenting banks while scrutinising / recognising cheques of drawee banks in an image-based processing scenario. In addition, certain desirable features are also being suggested which could be implemented by banks based on their need and risk perception. These include provision of mandatory minimum security features on cheque forms like quality of paper, watermark, bank’s logo in invisible ink, void pantograph, etc., and standardisation of field placements on cheques. It has since been decided to prescribe certain benchmarks towards achieving standardisation of cheques issued by banks across the country. The feedback from these institutions has been received and duly considered.ĥ. Recommendations of the Working Group were discussed internally as also forwarded to Indian Banks’ Association (IBA), National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and select banks for their views. commercial banks, paper manufacturers, security printers, etc., apart from Reserve Bank of India. The Working Group comprised various stakeholders viz. Against the above backdrop, a Working Group was set-up by the Reserve Bank of India for examining further standardisation of cheque forms and enhancement of security features therein. Growing use of multi-city and payable-at-par cheques for handling of cheques at any branches of a bank, introduction of Cheque Truncation System (CTS) at New Delhi for image-based cheque processing, increasing popularity of Speed Clearing for local processing of outstation cheques, etc., are a few aspects that led to looking into the need, if any, for prescription of certain minimum security features in cheques printed, issued and handled by banks and customers uniformly across the banking industry.Ĥ. Over a period of time, banks have added a variety of patterns and design of cheque forms to aid segmentation, branding, identification, etc., as also incorporated therein a number of security features to reduce the incidence of cheque misuse, tampering, alterations, etc. Standardisation of cheque forms (leaves) in terms of size, MICR band, quality of paper, etc., was one of the key factors that enabled mechanisation of cheque processing.ģ.

At the banks’ end too, cheques in MICR format have facilitated post-processing ease in operations, affording credit to customer accounts and reducing reconciliation issues, thus improving customer service.

Introduction of Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) technology during the mid-eighties has been the single-most important development responsible for making the cheque clearing popular and efficient – volume-wise, speed-wise and convenience-wise. Several measures have been initiated by Reserve Bank of India to ensure that this retail payment product functions in a safe and efficient manner.Ģ. During the period April-December 2009, clearing houses in the country have processed on an average around 4.5 million cheques every day. Paper-based cheque clearing continues to be one of the popular modes of initiating payment transactions in the country. Standardisation and Enhancement of Security Features in Cheque Forms


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
